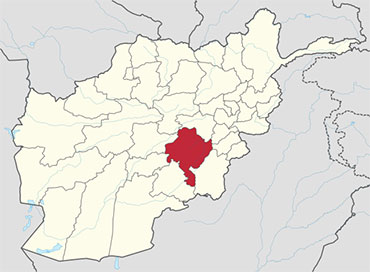
 Bamyan Province is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the central highlands of the country. Its terrain is mountainous or semi-mountainous. The province is divided into six districts, with the town of Bamyan serving as its capital. The province has a population of about 425,500. It is the largest province in the Hazarajat region of Afghanistan, and is the cultural capital of the Hazara ethnic group that predominates in the area.Its name can be translated as “The Place of Shining Light”. In antiquity, central Afghanistan was strategically placed to thrive from the Silk Road caravans which criss-crossed the region trading between the Roman Empire, China, Central and South Asia. Bamyan was a stopping off point for many travellers. It was here where elements of Greek and Buddhist art were combined into a unique classical style, known as Greco-Buddhist art.
Bamyan Province is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the central highlands of the country. Its terrain is mountainous or semi-mountainous. The province is divided into six districts, with the town of Bamyan serving as its capital. The province has a population of about 425,500. It is the largest province in the Hazarajat region of Afghanistan, and is the cultural capital of the Hazara ethnic group that predominates in the area.Its name can be translated as “The Place of Shining Light”. In antiquity, central Afghanistan was strategically placed to thrive from the Silk Road caravans which criss-crossed the region trading between the Roman Empire, China, Central and South Asia. Bamyan was a stopping off point for many travellers. It was here where elements of Greek and Buddhist art were combined into a unique classical style, known as Greco-Buddhist art.
The province has several famous historical sites, including the famous Buddha statues with more than 3,000 caves around it, the Band-e Amir National Park, Dara-i-Ajhdar, Gholghola and Zakhak ancient towns, the Feroz Bahar, Astopa, Klegan, Gaohargin, Kaferan and Cheldukhtaran.
Bamyan province under Mauryan Empire rule
The Bamyan province territory fell to the Maurya Empire, which was led by Chandragupta Maurya. The Mauryas introduced Hinduism and Buddhism to region, and were planning to capture more territory of Central Asia until they faced local Greco-Bactrian forces. Seleucus is said to have reach a peace treaty with Chandragupta by given control of the territory south of the Hindu Kush to the Mauryas upon intermarriage and 500 elephants.
Maurya Empire under Ashoka the Great
Alexander took these away from the Indo-Aryans and established settlements of his own, but Seleucus Nicator gave them to Sandrocottus (Chandragupta), upon terms of intermarriage and of receiving in exchange 500 elephants.
— Strabo, 64 BCE–24 CE
Some time after, as he was going to war with the generals of Alexander, a wild elephant of great bulk presented itself before him of its own accord, and, as if tamed down to gentleness, took him on its back, and became his guide in the war, and conspicuous in fields of battle. Sandrocottus, having thus acquired a throne, was in possession of India, when Seleucus was laying the foundations of his future greatness; who, after making a league with him, and settling his affairs in the east, proceeded to join in the war against Antigonus. As soon as the forces, therefore, of all the confederates were united, a battle was fought, in which Antigonus was slain, and his son Demetrius put to flight.
— Junianus Justinus
Newly excavated Buddhist stupa at Mes Aynak in Logar Province of Afghanistan. Similar stupas have been discovered in neighboring Ghazni Province, including in the northern Samangan Province.
Having consolidated power in the northwest, Chandragupta pushed east towards the Nanda Empire. Afghanistan’s significant ancient tangible and intangible Buddhist heritage is recorded through wide-ranging archeological finds, including religious and artistic remnants. Buddhist doctrines are reported to have reached as far as Balkh even during the life of the Buddha (563 BCE to 483 BCE), as recorded by Husang Tsang.
In this context a legend recorded by Husang Tsang refers to the first two lay disciples of Buddha, Trapusa and Bhallika responsible for introducing Buddhism in that country. Originally these two were merchants of the kingdom of Balhika, as the name Bhalluka or Bhallika probably suggests the association of one with that country. They had gone to India for trade and had happened to be at Bodhgaya when the Buddha had just attained enlightenment.
The region was ruled by the Achaemenids. In 330 BC, Alexander the Great seized the area but left it to Seleucids to rule. The area south of the Hindu Kush was given to the Mauryas who introduced Buddhism. It became the site of an early Buddhist monastery from which Bamyan takes its name from the Sanskrit varmayana (“coloured”). Many statues of Buddha were carved into the sides of cliffs facing Bamyan city. The two most prominent of these statues were standing Buddhas, now known as the Buddhas of Bamyan, measuring 55 and 37 meters high respectively, that were the largest examples of standing Buddha carvings in the world. They were probably erected in the 4th or 5th century A.D. They were cultural landmarks for many years and are listed among UNESCO’s World Heritage Sites. In March 2001 the Taliban government decreed that the statues were idolatrous and ordered them to be demolished with anti-aircraft artillery and explosives.
Bilingual (Greek and Aramaic) edict by Emperor Ashoka from the 3rd century BCE discovered in the southern city of Kandahar
Archaeological exploration done in the 20th century suggests that the geographical area of Afghanistan has been closely connected by culture and trade with its neighbors to the east, west, and north. Artifacts typical of the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic, Bronze, and Iron ages have been found in Afghanistan. Urban civilization is believed to have begun as early as 3000 BCE, and the early city of Mundigak (near Kandahar in the south of the country) may have been a colony of the nearby Indus Valley Civilization.
One of the Buddhas of Bamiyan. Buddhism was widespread in the region before the Islamic conquest of Afghanistan.
After 2000 BCE, successive waves of semi-nomadic people from Central Asia began moving south into Afghanistan; among them were many Indo-European-speaking Indo-Iranians. These tribes later migrated further south to India, west to what is now Iran, and towards Europe via the area north of the Caspian Sea. The region as a whole was called Ariana.
The people shared similar culture with other Indo-Iranians. The ancient religion of Kafiristan survived here until the 19th century. Another religion, Zoroastrianism is believed by some to have originated in what is now Afghanistan between 1800 and 800 BCE, as its founder Zoroaster is thought to have lived and died in Balkh. Ancient Eastern Iranian languages may have been spoken in the region around the time of the rise of Zoroastrianism. By the middle of the 6th century BCE, the Achaemenid Persians overthrew the Medes and incorporated Arachosia, Aria, and Bactria within its eastern boundaries. An inscription on the tombstone of King Darius I of Persia mentions the Kabul Valley in a list of the 29 countries that he had conquered.
By the 7th century, when the Arabs first arrived, it was under the control of the Kabul Shahi before being conquered in the name of Islam by the Saffarids in the 9th century. It fell to the Ghaznavids followed by the Ghurids before the Mongol invasion in the 13th century. The area was ruled by Arghun Khan of Ilkhanate, later by the Timurids and Mughals.
In 1709, when the Hotaki dynasty rose to power in Kandahar and defeated the Persian Safavids, Bamyan was under the Mughal Empire influence until Ahmad Shah Durrani made it become part of the Afghan Durrani Empire, which became to what is now the modern state of Afghanistan.
During the 1980s Soviet war in Afghanistan, the Hazara rebel leader Abdul Ali Mazari began spreading influence. He was supported by Iranian politicians. He founded the Hezbe Wahdat political party in 1989 and was killed by Taliban forces. By 1995, Bamyan province was under the control of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (Taliban government). They were toppled by US-led forces in late 2001.
Recent History
After the formation of the Karzai administration, Bamyan became the focus of rebuilding.
The Buddhist remains at Bamyan were included on the 2008 World Monuments Watch List of the 100 Most Endangered Sites by the World Monuments Fund. It is hoped that the listing will put continued national and international attention on the site as a whole (including, but not limited to, the statues) in order to ensure its long-term preservation, and to make certain that future restoration efforts maintain the authenticity of the site and that proper preservation practices are followed. Bamyan is also known as the capital of Daizangi and for its natural beauty.
It is recognised as one of the safest provinces in the country, which has allowed for civil rebuilding. Bamyan served as the base of operations for the New Zealand peacekeeping force, a Provincial Reconstruction Team codenamed Task Group Crib, which was part of the network of Provincial Reconstruction Teams throughout Afghanistan.
Demographics
The total population of Bamyan province is around 425,500. It is a multi-ethnic tribal society. According to the Naval Postgraduate School, the ethnic groups of the province are as follows: 67.4% Hazara; 16% Sadat; 15.7% Tajik; 0.5% Tatar; 0.2% Qizilbash; and 0.1% Pashtun.
Districts
Bamyan province is divided in to 7 districts.
| Province | Population | Area |
|---|---|---|
| Bamyan | 9,001,028 | |
| Kahmard | 31,042 | |
| Panjab | 48,397 | |
| Saraik | 23,215 | |
| Shibar | 22,933 | |
| Waras | 82,119 | |
| Nayak | 100,158 |